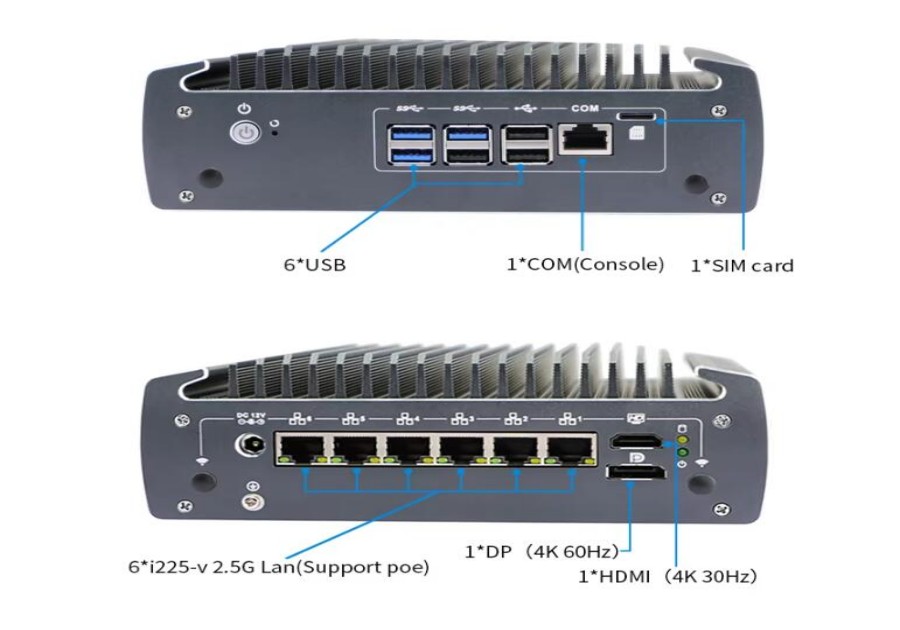
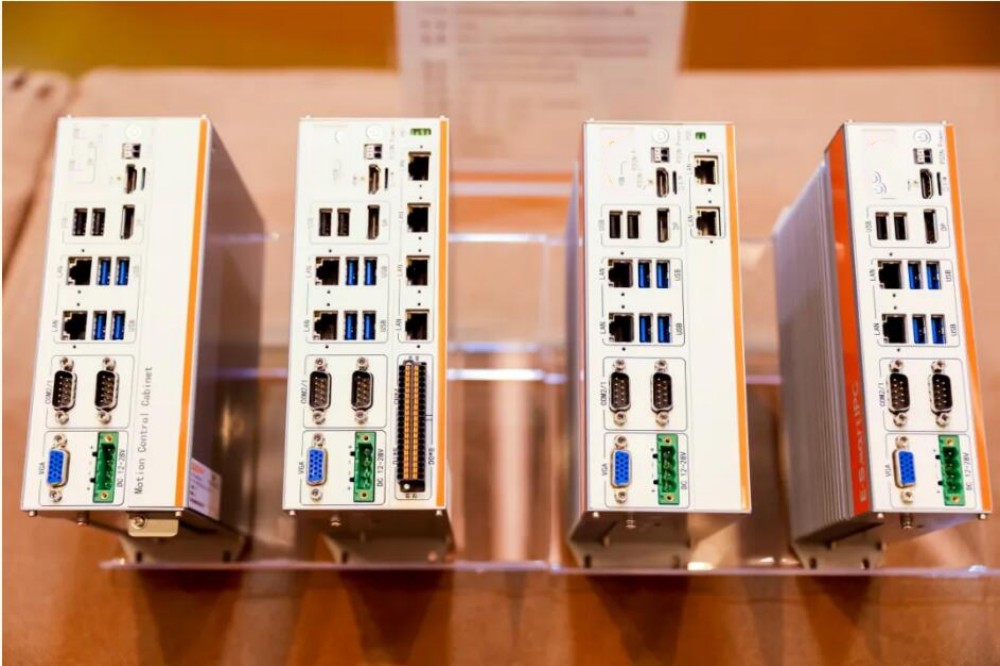
Industrial Computers: How to Solve Problems for Customers
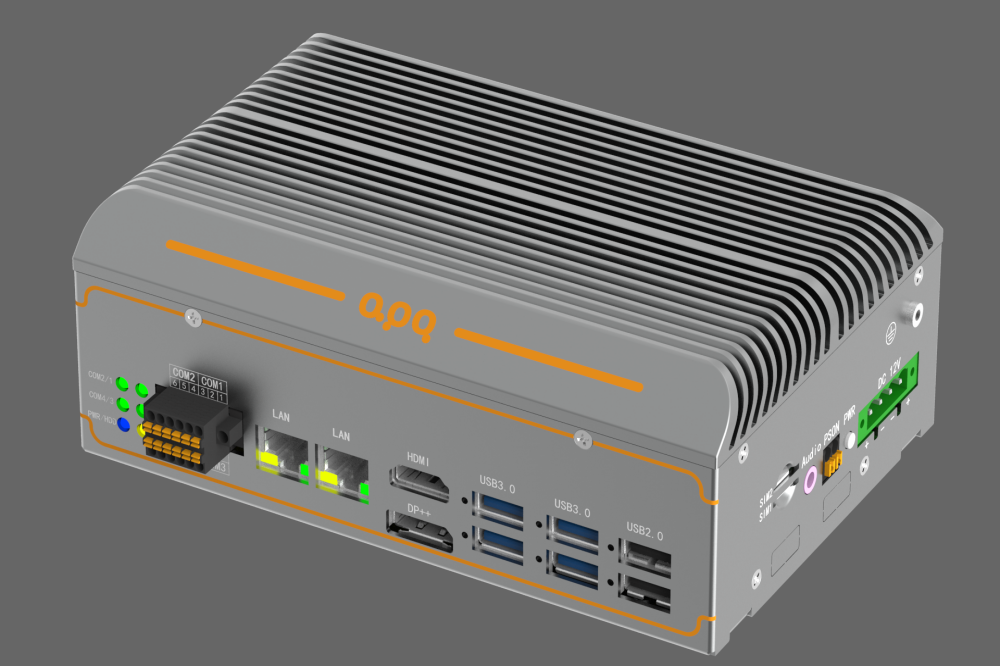
Industrial computers are specialized systems designed to operate in challenging environments, providing reliable and robust performance. As businesses across various sectors increasingly rely on automation and advanced technology, industrial computers have become essential tools. Here are some key problems industrial computers solve for customers:


1. Harsh Environmental Conditions
Problem: Many industries, such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and mining, operate in environments with extreme temperatures, dust, moisture, and vibrations. Standard computers cannot withstand these conditions, leading to frequent breakdowns and costly downtime.
Solution: Industrial computers are built to endure harsh conditions. They are designed with rugged enclosures, fanless cooling systems, and are often sealed to protect against dust and moisture. These features ensure continuous operation in extreme environments, reducing maintenance costs and increasing uptime.
2. Reliability and Longevity
Problem: Industrial applications require systems that can run continuously without failure. Frequent hardware failures can lead to significant financial losses and operational disruptions.
Solution: Industrial computers are engineered for high reliability and long service life. They use industrial-grade components that are more durable than consumer-grade parts. Additionally, these computers often come with extended warranties and support, ensuring long-term reliability.
3. Real-Time Data Processing
Problem: In industries like automation, transportation, and energy, real-time data processing is crucial. Delays or inaccuracies in data processing can lead to inefficiencies and safety hazards.
Solution: Industrial computers are equipped with powerful processors and specialized software that enable real-time data processing. This capability allows for immediate decision-making and adjustments, enhancing efficiency and safety in critical operations.
4. Customizability and Scalability
Problem: Different industries have unique requirements that standard computers cannot meet. Additionally, as businesses grow, their computing needs evolve.
Solution: Industrial computers offer high levels of customizability. Customers can choose specific components, configurations, and form factors to meet their exact needs. Furthermore, these systems are scalable, allowing businesses to upgrade or expand their computing capabilities as needed.
5. Integration with Legacy Systems
Problem: Many industrial operations rely on legacy systems and equipment that may not be compatible with modern computing solutions.
Solution: Industrial computers are designed to integrate seamlessly with legacy systems. They support a wide range of connectivity options and communication protocols, ensuring compatibility with existing equipment. This integration capability helps businesses modernize their operations without the need for costly overhauls.
6. Security and Data Protection
Problem: Industrial environments are increasingly targeted by cyber threats. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the security of industrial control systems is a major concern.
Solution: Industrial computers come with advanced security features, including hardware encryption, secure boot, and intrusion detection. These measures protect against cyber-attacks and unauthorized access, ensuring the safety and integrity of critical data and systems.
7. Cost Efficiency
Problem: High upfront costs and frequent maintenance of computing systems can strain budgets, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Solution: Although industrial computers may have a higher initial cost than consumer-grade systems, their durability, reliability, and low maintenance requirements result in long-term cost savings. Businesses benefit from reduced downtime, fewer repairs, and extended system lifespans, making industrial computers a cost-effective investment.

Conclusion
Industrial computers are indispensable in modern industrial operations, addressing critical challenges such as harsh environments, the need for reliability, real-time data processing, and security concerns. By providing robust, customizable, and secure solutions, industrial computers help businesses enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and stay competitive in an increasingly automated and data-driven world.